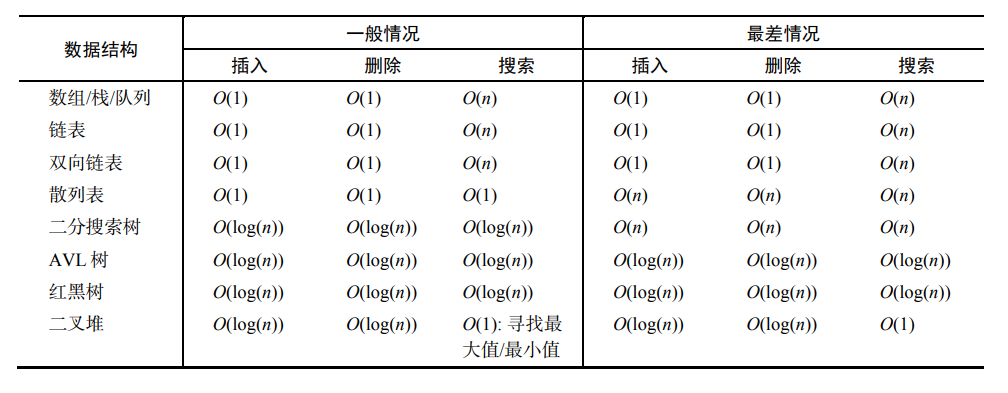
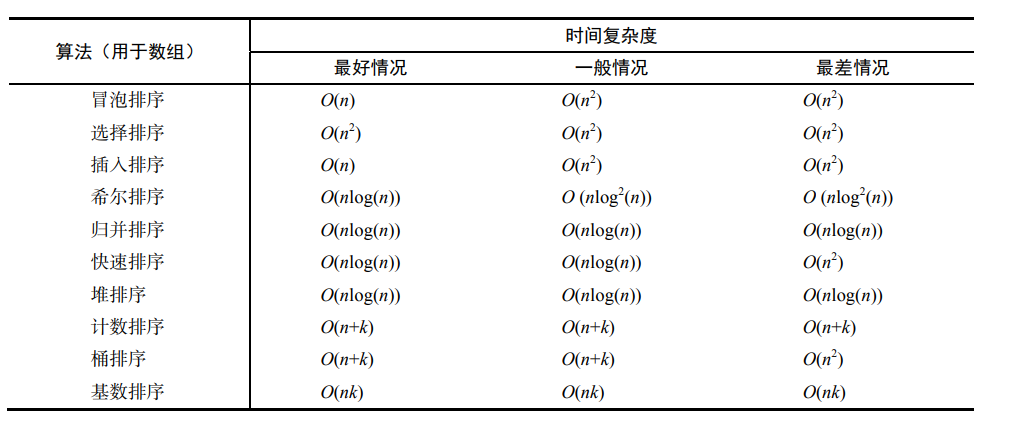
[toc]
JS数据结构与算法
一. 初识数据结构与算法
- “数据结构是数据对象,以及存在于该对象的实例和组成实例的数据元素之间的各种联系。这些联系可以通过定义相关的函数来给出。”——Sartaj Sahni,《数据结构、算法与应用》
- “数据结构是ADT(抽象数据类型 Abstract DataType)的物理实现。”—— Clifford A.Shaffer,《数据结构与算法分析》
- “数据结构(data structure)是计算机中存储、组织数据的方式。通常情况下,精心选择的数据结构可以带来最优效率的算法。” ——中文维基百科
1. 常见的数据结构
- 数组(Aarray)
- 栈(Stack)
- 链表(Linked List)
- 图(Graph)
- 散列表(Hash)
- 队列(Queue)
- 堆(Heap)
- 树(Tree)
2. 算法
算法(Algorithm)是指解题方案的准确而完整的描述,是一系列解决问题的清晰指令,算法代表着用系统的方法描述解决问题的策略机制。也就是说,能够对一定规范的输入,在有限时间内获得所要求的输出。如果一个算法有缺陷,或不适合于某个问题,执行这个算法将不会解决这个问题。不同的算法可能用不同的时间,空间或效率来完成同样的任务。一个算法的优劣可以用空间复杂度与时间复杂度来衡量。
二. 数组结构
什么是数组?
字面理解就是 数字的组合
其实不太准确,准确的来说数组是一个 数据的集合
也就是我们把一些数据放在一个盒子里面,按照顺序排好
javascript[1, 2, 3, "hello", true, false];这个东西就是一个数组,存储着一些数据的集合
数据类型分类
number/string/boolean/undefined/null/object/function/array/ ...数组也是数据类型中的一种
我们简单的把所有数据类型分为两个大类 基本数据类型 和 复杂数据类型
基本数据类型:
number/string/boolean/undefined/null复杂数据类型:
object/function/array/ ...
1 创建一个数组
- 数组就是一个
[] - 在
[]里面存储着各种各样的数据,按照顺序依次排好
字面量创建一个数组
直接使用
[]的方式创建一个数组javascript// 创建一个空数组 var arr1 = []; // 创建一个有内容的数组 var arr2 = [1, 2, 3];
内置构造函数创建数组
使用
js的内置构造函数Array创建一个数组javascript// 创建一个空数组 var arr1 = new Array(); // 创建一个长度为 10 的数组 var arr2 = new Array(10); // 创建一个有内容的数组 var arr3 = new Array(1, 2, 3);
2 数组的 length
length: 长度的意思length就是表示数组的长度,数组里面有多少个成员,length就是多少javascript// 创建一个数组 var arr = [1, 2, 3]; console.log(arr.length); // 3
3 数组的索引
索引,也叫做下标,是指一个数据在数组里面排在第几个的位置
注意: 在所有的语言里面,索引都是从 0 开始的
在
js里面也一样,数组的索引从 0 开始javascript// 创建一个数组 var arr = ["hello", "world"];上面这个数组中,第 0 个 数据就是字符串
hello,第 1 个 数据就是字符串world想获取数组中的第几个就使用
数组[索引]来获取javascriptvar arr = ["hello", "world"]; console.log(arr[0]); // hello console.log(arr[1]); // world
4 数组的常用方法
数组是一个复杂数据类型,我们在操作它的时候就不能再想基本数据类型一样操作了
比如我们想改变一个数组
javascript// 创建一个数组 var arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 我们想把数组变成只有 1 和 2 arr = [1, 2];- 这样肯定是不合理,因为这样不是在改变之前的数组
- 相当于心弄了一个数组给到
arr这个变量了 - 相当于把
arr里面存储的地址给换了,也就是把存储空间换掉了,而不是在之前的空间里面修改 - 所以我们就需要借助一些方法,在不改变存储空间的情况下,把存储空间里面的数据改变了
数组常用方法之 push
push是用来在数组的末尾追加一个元素javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 push 方法追加一个元素在末尾 arr.push(4); console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
数组常用方法之 pop
pop是用来删除数组末尾的一个元素javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 pop 方法删除末尾的一个元素 arr.pop(); console.log(arr); // [1, 2]
数组常用方法之 unshift
unshift是在数组的最前面添加一个元素javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 unshift 方法想数组的最前面添加一个元素 arr.unshift(4); console.log(arr); // [4, 1, 2, 3]
数组常用方法之 shift
shift是删除数组最前面的一个元素javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 shift 方法删除数组最前面的一个元素 arr.shift(); console.log(arr); // [2, 3]
数组常用方法之 splice /splaɪs/
splice是截取数组中的某些内容,按照数组的索引来截取语法:
splice(从哪一个索引位置开始,截取多少个,替换的新元素)(第三个参数可以不写)javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // 使用 splice 方法截取数组 arr.splice(1, 2); console.log(arr); // [1, 4, 5]arr.splice(1, 2)表示从索引 1 开始截取 2 个内容- 第三个参数没有写,就是没有新内容替换掉截取位置
javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // 使用 splice 方法截取数组 arr.splice(1, 2, "我是新内容"); console.log(arr); // [1, '我是新内容', 4, 5]arr.splice(1, 2, '我是新内容')表示从索引 1 开始截取 2 个内容- 然后用第三个参数把截取完空出来的位置填充
第三个参数可以加多个数:

数组常用方法之 reverse
reverse是用来反转数组使用的javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 reverse 方法来反转数组 arr.reverse(); console.log(arr); // [3, 2, 1]
数组常用方法之 sort
sort是用来给数组排序的javascriptvar arr = [2, 3, 1]; // 使用 sort 方法给数组排序 arr.sort(); console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3]- 这个只是一个基本的简单用法
sort也可以排对象

数组常用方法之 concat
concat是把多个数组进行拼接和之前的方法有一些不一样的地方,就是
concat不会改变原始数组,而是返回一个新的数组javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 concat 方法拼接数组 var newArr = arr.concat([4, 5, 6]); console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3] console.log(newArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]- 注意:
concat方法不会改变原始数组
- 注意:
可以接数组也可以接直接参数

数组常用方法之 join
join是把数组里面的每一项内容链接起来,变成一个字符串可以自己定义每一项之间链接的内容
join(要以什么内容链接)不会改变原始数组,而是把链接好的字符串返回
javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 join 链接数组 var str = arr.join("-"); console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3] console.log(str); // 1-2-3- 注意: join 方法不会改变原始数组,而是返回链接好的字符串
数组常用方法之 indexOf
indexOf用来找到数组中某一项的索引语法:
indexOf(你要找的数组中的项)javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // 使用 indexOf 超找数组中的某一项 var index = arr.indexOf(3); console.log(index); // 2- 我们要找的是数组中值为 3 的那一项
- 返回的就是值为 3 的那一项在该数组中的索引
如果你要找的内容在数组中没有,那么就会返回 -1
javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // 使用 indexOf 超找数组中的某一项 var index = arr.indexOf(10); console.log(index); // -1- 你要找的值在数组中不存在,那么就会返回 -1
数组常用方法之incluedes

数组方法之find findLast
find从前往后找,findlast从后往前找 返回具体值

以及findIndex和findLastIndex
返回索引值
数组常用方法之 forEach
和
for循环一个作用,就是用来遍历数组的语法:
arr.forEach(function (item, index, arr) {})javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 forEach 遍历数组 arr.forEach(function (item, index, arr) { // item 就是数组中的每一项 // index 就是数组的索引 // arr 就是原始数组 console.log("数组的第 " + index + " 项的值是 " + item + ",原始数组是", arr); });forEach()的时候传递的那个函数,会根据数组的长度执行- 数组的长度是多少,这个函数就会执行多少回

数组常用方法之 map
和
forEach类似,只不过可以对数组中的每一项进行操作,返回一个新的数组javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3] // 使用 map 遍历数组 var newArr = arr.map(function (item, index, arr) { // item 就是数组中的每一项 // index 就是数组的索引 // arr 就是原始数组 return item + 10 }) console.log(newArr) // [11, 12, 13] 箭头函数写法: let res = arr.map(ietm=>ietm+1)
数组常用方法之 filter /ˈfɪltə(r)/
和
map的使用方式类似,按照我们的条件来筛选数组把原始数组中满足条件的筛选出来,组成一个新的数组返回
javascriptvar arr = [1, 2, 3]; // 使用 filter 过滤数组 var newArr = arr.filter(function (item, index, arr) { // item 就是数组中的每一项 // index 就是数组的索引 // arr 就是原始数组 return item > 1; }); console.log(newArr); // [2, 3]- 我们设置的条件就是
> 1 - 返回的新数组就会是原始数组中所有
> 1的项
- 我们设置的条件就是
数组方法之 every

判断每一项是否都满足条件,满足返回true,否则返回false
数组方法之some

有一项满足即为true
数组方法之reduce
累加

迭代器iterator /ɪtəˈreɪtə/

数组方法之entries


以及,.keys 拿到的是键, .values拿到的就是值
数组之Array.from()
function test() {
console.log(Array.from(arguments));
}
test(1, 2, 3);arguments对象:- 在 JavaScript 中,每个函数内部都可以访问一个特殊的
arguments对象 arguments是一个类数组对象,包含所有传递给函数的参数- 即使函数没有定义参数,仍然可以通过
arguments访问传入的参数
- 在 JavaScript 中,每个函数内部都可以访问一个特殊的
Array.from(arguments):arguments是一个类数组对象(有 length 属性和索引元素,但不是真正的数组)Array.from()方法将类数组对象或可迭代对象转换为真正的数组- 这里将
arguments转换为真正的数组
- 函数调用:
test(1, 2, 3)调用了test函数并传入了三个参数 - 输出结果:
(3) [1, 2, 3](3)表示数组长度为 3[1, 2, 3]是转换后的数组内容
二维数组

三. 栈结构
1.认识栈结构
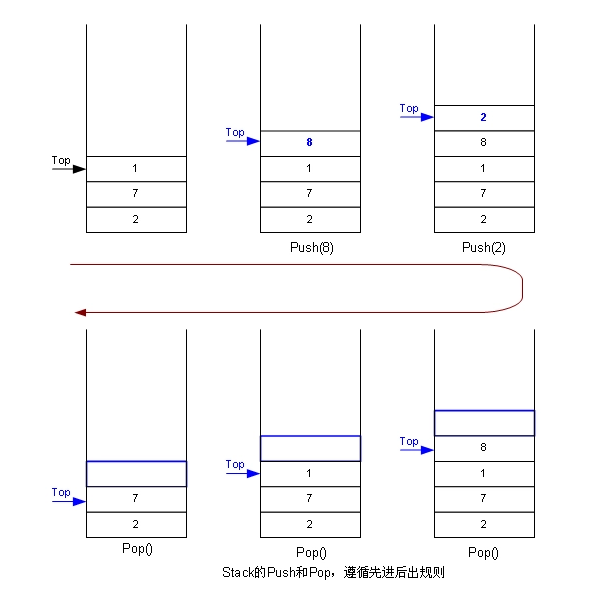
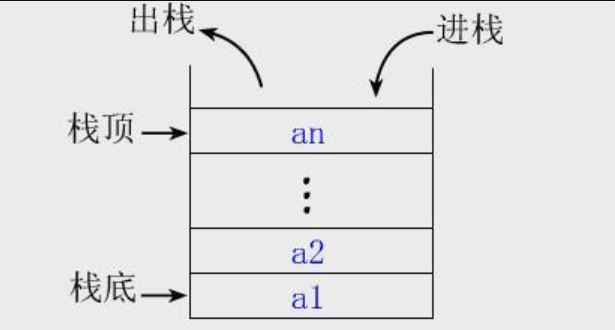
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
特点:后进先出即Last in First Out(LIFO)。
函数调用栈
数组与栈区别
| 特性 | 数组 (Array) | 栈 (Stack) |
|---|---|---|
| 访问方式 | 随机访问(可通过索引访问任意元素) | 只能访问栈顶元素(LIFO原则) |
| 操作 | 支持多种操作(增删改查任意位置) | 只允许在栈顶进行push/pop操作 |
| 灵活性 | 高度灵活 | 受限的操作集合 |
| 实现 | 基础数据结构 | 通常基于数组或链表实现 |
| 大小 | 通常动态可变 | 可以是固定或动态大小 |
2. 封装栈结构
push 添加一个元素到栈顶
pop 出栈
peek 返回栈顶
isEmpty() clear() size() toString()
class Stack{
// constructor(){
// this.items = []
// }
#items = []
push(data){
this.#items.push(data)
}
pop(){
return this.#items.pop()
}
peek(){
// return this.items[this.items.length-1]
return this.#items.at(-1) //找最后一个元素
}
isEmpty(){
return this.#items.length===0
}
size(){
return this.#items.length
}
clear(){
this.#items = []
}
toString(){
return this.#items.join("") 转字符串
}
}3. 应用
3-1 十进制转二进制 辗转相除法/除二取余
function convert(decNumber) {
//convert 转变 /kənˈvɜːt/
let remStack = new Stack();
let number = decNumber;
let rem;
let string = "";
while (number > 0) {
rem = number % 2; //取余数
remStack.push(rem);
number = Math.floor(number / 2); //向下取整
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()) {
string += remStack.pop();
}
return string;
}3-2 进制转换法
function convert(decNumber, base) {
//base是进制数
let remStack = new Stack();
let number = decNumber;
let rem;
let string = "";
let baseStr = "0123456789ABCDEF"; //为了兼容十六进制
while (number > 0) {
rem = number % base;
remStack.push(rem);
number = Math.floor(number / base);
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()) {
string += baseStr[remStack.pop()]; //取baseString的索引值
}
return string;
}四. 队列
1.队列是什么?
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。队列中没有元素时,称为空队列。
队列的数据元素又称为队列元素。在队列中插入一个队列元素称为入队,从队列中删除一个队列元素称为出队。因为队列只允许在一端插入,在另一端删除,所以只有最早进入队列的元素才能最先从队列中删除,故队列又称为先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)线性表。

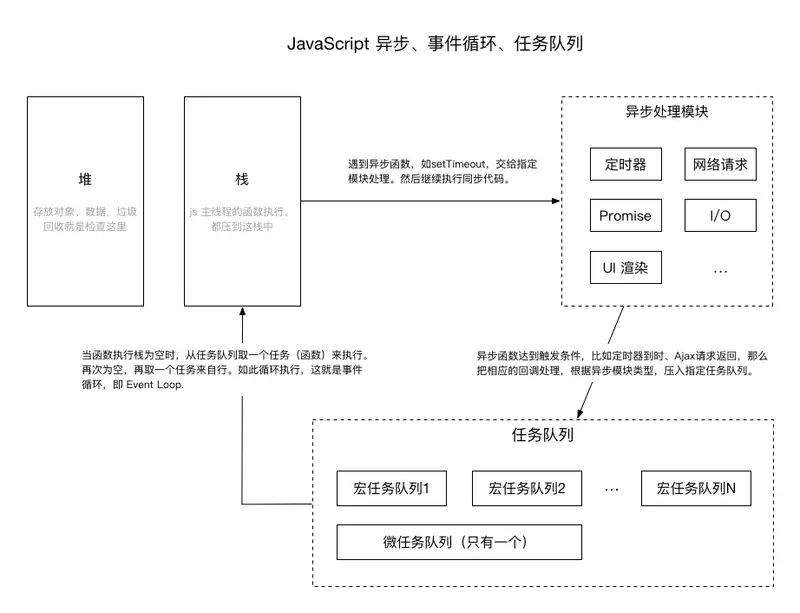
2.队列的封装
class Queue { /kjuː/
#items = {}
#count = 0 //当前值索引
#lowCount = 0 //记录队头索引
dequeue() {
if(this.isEmpty()){
return undefined
}
let res = this.#items[this.#lowCount]
delete this.#items[this.#lowCount]
this.#lowCount++
return res
}
enqueue(data) {
this.#items[this.#count] = data
this.#count++
}
front() {
// return this.#items.at(0)
return this.#items[this.#lowCount]
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0
}
size() {
return this.#count-this.#lowCount
}
clear() {
this.#items = {}
this.#count = 0;
this.#lowCount = 0
}
toString() {
let str = ""
for(let i =this.#lowCount;i<this.#count;i++){
str += `${this.#items[i]} `
}
return str
}
}补充:
delete的基本性质
- 操作对象:专门用于删除对象的属性
- 语法:
delete object.property或delete object['property'] - 返回值:返回
true(删除成功)或false(严格模式下删除不可配置属性会报错)
- 在数组上的表现
虽然 JavaScript 中数组也是对象,但对数组使用 delete 会有特殊表现:
javascript
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
delete arr[1]; // 删除索引为1的元素
console.log(arr); // ['a', empty, 'c']
console.log(arr[1]); // undefined
console.log(arr.length); // 仍然是3关键特点:
- 不会改变数组长度
- 只是将指定位置的值设为
empty(稀疏数组) - 被删除的索引位置变为"空位",但不是真正的移除
- 在普通对象上的表现
javascript
const obj = {x: 1, y: 2, z: 3};
delete obj.y;
console.log(obj); // {x: 1, z: 3}
console.log('y' in obj); // false关键特点:
- 完全移除指定属性
- 对象结构会改变
- 后续访问返回
undefined
- 为什么队列实现使用对象而非数组
在您看到的队列实现中,作者选择使用普通对象 {} 而不是数组 [] 有几个原因:
使用对象 + delete 的优势:
- 真正的属性移除:
delete会完全移除对象属性 - 不需要重新索引:不像数组
shift()需要移动所有元素 - 指针控制灵活:通过
#lowCount和#count可以精确控制队列范围
3. 队列的应用-击鼓传花
function game(list, num) {
let queue = new Queue();
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
queue.enqueue(list[i]);
}
while (queue.size() > 1) {
for (let i = 0; i < num; i++) {
queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue()); //从队头dequeue
}
console.log(queue.dequeue(), "淘汰了");
}
return {
winner: queue.dequeue(),
};
}
game(["kerwin", "tiechui", "xiaoming", "gangdaner", "guludunzi"], 7);4. 双端队列
class DeQueue {
//double ended queue
#items = {};
#lowCount = 0;
#count = 0;
// 前删
removeFront() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
let res = this.#items[this.#lowCount];
delete this.#items[this.#lowCount];
this.#lowCount++;
return res;
}
//后加
addBack(data) {
this.#items[this.#count] = data;
this.#count++;
}
//前加
addFront(data) {
//1.如果为空 直接从队尾加入
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.addBack(data);
} else if (this.#lowCount > 0) {
// 移动队首指针,往前移动一位 指向新增加的值
this.#lowCount--;
this.#items[this.#lowCount] = data;
} else {
//lowCount = 0
for (let i = this.#count; i > 0; i--) {
this.#items[i] = this.#items[i - 1];
}
this.#count++;
this.#lowCount = 0;
this.#items[0] = data;
}
}
//后删
removeBack() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
this.#count--;
const result = this.#items[this.#count];
delete this.#items[this.#count];
return result;
}
//查找队头元素
peekFront() {
return this.#items[this.#lowCount];
}
//查找队尾元素
peekBack() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
return this.#items[this.#count - 1];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return this.#count - this.#lowCount;
}
clear() {
this.#items = {};
this.#count = 0;
this.#lowCount = 0;
}
toString() {
let str = "";
for (let i = this.#lowCount; i < this.#count; i++) {
str += `${this.#items[i]} `;
}
return str;
}
}
回文检查
字符串要去空格及统一大小写



五. 链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
使用链表结构可以克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。
链表的特点
1.插入、删除数据效率高O(1)级别(只需更改指针指向即可),随机访问效率低O(n)级别(需要从链头至链尾进行遍历)。2.和数组相比,内存空间消耗更大,因为每个存储数据的节点都需要额外的空间存储后继指针。
1. 单链表
每个节点只包含一个指针,即后继指针。
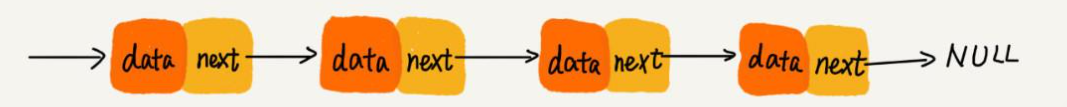
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.count = 0;
}
push(element) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current;
//header是空的时候
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
while (current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
this.count++;
}
//指定位置删除
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next; //把第二个直接接head,就可以把第一个去掉
} else {
let previous;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return;
}
//传入索引值,返回结点
getNodeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let node = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return;
}
//使用getNodeAt实现removeAt
removeAt2(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1); //就是这里,注意是要上一个节点
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return;
}
//判断传入的值和当前索引的值是否一致
equalFn(a, b) {
return JSON.stringify(a) === JSON.stringify(b);
//可以用imumutable第三方库来实现比较
}
//找到传入值对应的索引
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.count; i++) {
//判断传入的值和当前索引的值是否一致,一致则返回当前索引值
if (this.equalFn(element, current.element)) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
//根据传入的值来删除,而不是根据索引
remove(element) {
//调用根据索引删除对应项的方法
const index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
//在任意位置插入一个元素
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element);
if (index === 0) {
const current = this.head;
node.next = current;
this.head = node;
} else {
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
const current = previous.next;
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
}注意:{a:1}和{a:1}是不相等的
在 JavaScript 中,{a:1} == {a:1} 或 {a:1} === {a:1} 都会返回 false,这是因为:
- 对象是引用类型:当比较两个对象时,比较的是它们在内存中的引用(地址),而不是它们的内容(属性)。即使两个对象的内容完全相同,只要它们是两个不同的实例,就不相等。
- 每次
{}都创建一个新对象:- 每次写
{a:1},JavaScript 都会在内存中创建一个新的对象。 - 即使内容相同,这两个对象的引用(内存地址)也不同。
- 每次写
例子说明
const obj1 = { a: 1 };
const obj2 = { a: 1 };
const obj3 = obj1;
console.log(obj1 === obj2); // false(不同引用)
console.log(obj1 === obj3); // true(相同引用)

用链表实现回文

用链表实现击鼓传花

2. 双向链表
节点除了存储数据外,还有两个指针分别指向前一个节点地址(前驱指针prev)和下一个节点地址(后继指针next)。

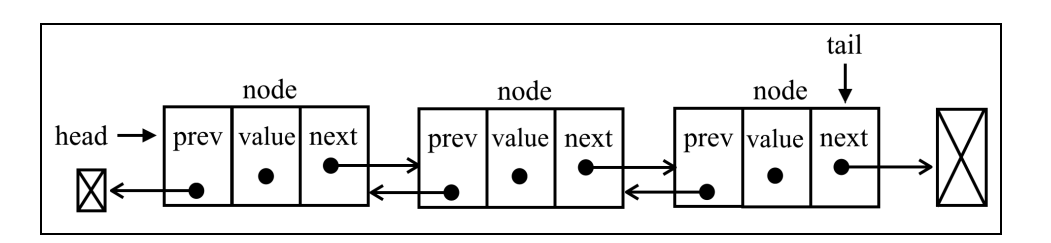
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element) {
super(element);
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
push(element) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.count++;
}
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == null) {
//此时链表为空,没有
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
//此时li
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
//链尾插入
} else if (index === this.count) {
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else {
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.count === 1) {
// {2}
this.tail = undefined;
} else {
this.head.prev = undefined;
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = undefined;
} else {
current = this.getNodeAt(index);
const previous = current.prev;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous; // NEW
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
getTail() {
return this.tail;
}
}3. 循环链表
循环链表和链表之间唯一的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用 undefined,而是指向第一个元素(head)
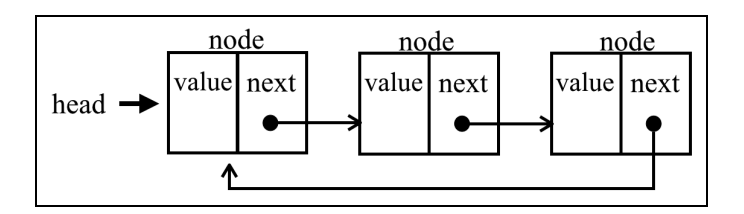
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
}
push(element) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current;
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.getNodeAt(this.size() - 1); //先找到最后一个节点
current.next = node;
}
node.next = this.head;
this.count++;
}
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == null) {
// if no node in list
this.head = node;
node.next = this.head;
} else {
node.next = current;
current = this.getNodeAt(this.size() - 1);
// update last element
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = undefined;
} else {
let last = this.getNodeAt(this.size() - 1);
this.head = this.head.next;
last.next = this.head;
}
} else {
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next; // 如果删的是最后一个也不怕,current.next 是head
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
}
不能先赋值给head再取最后的节点元素,内容是错乱的
六. 集合
集合是由一组无序且唯一(即不能重复)的项组成的。
1.集合类
class KerwinSet {
constructor() {
this.items = {};
}
add(element) {
if (!this.has(element)) {
this.items[element] = element;
return true;
}
return false;
}
delete(element) {
if (this.has(element)) {
delete this.items[element];
return true;
}
return false;
}
clear() {
this.items = {};
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length;
}
values() {
return Object.values(this.items);
}
has(element) {
return element in this.items;
}
}2.ES6的Set
var myset = new Set();
myset.add(100);
myset.add(200);
myset.size; //这里是属性
myset.values();
myset.delete(100);
myset.clear();
myiter是一个迭代器
3.集合的运算
并集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中所有元素的新集合。
交集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中共有元素的新集合。
差集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含所有存在于第一个集合且不存在于第二个集 合的元素的新集合。
取并集:

取交集:

取差集:

七. 字典
字典和集合很相似,集合以[值,值]的形式存储元素,字 典则是以[键,值]的形式来存储元素。字典也称作映射、符号表或关联数组。
1.字典的封装
class Dictionary {
constructor() {
this.table = {};
}
//转换成字符串
toStrFn(item) {
if (item === null) {
return "NULL";
} else if (item === undefined) {
return "UNDEFINED";
} else if (typeof item === "string" || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`; //字符串要放在单引号里
}
return JSON.stringify(item);
}
//是否有值
hasKey(key) {
return this.table[this.toStrFn(key)] != null; //不用双等于,并不判断类型
}
set(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
this.table[tableKey] = new ValuePair(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
remove(key) {
if (this.hasKey(key)) {
delete this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const valuePair = this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
//它会以数组形式返回字典中的所有 valuePair 对象。
keyValues() {
return Object.values(this.table);
}
keys() {
return this.keyValues().map((valuePair) => valuePair.key);
}
values() {
return this.keyValues().map((valuePair) => valuePair.value);
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
forEach(callbackFn) {
const valuePairs = this.keyValues();
for (let i = 0; i < valuePairs.length; i++) {
callbackFn(valuePairs[i].key, valuePairs[i].value);
}
}
}
//使对象的键可以保存下来
class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
var mymap = new Dictionary();
举例应用:

foreach举例应用:


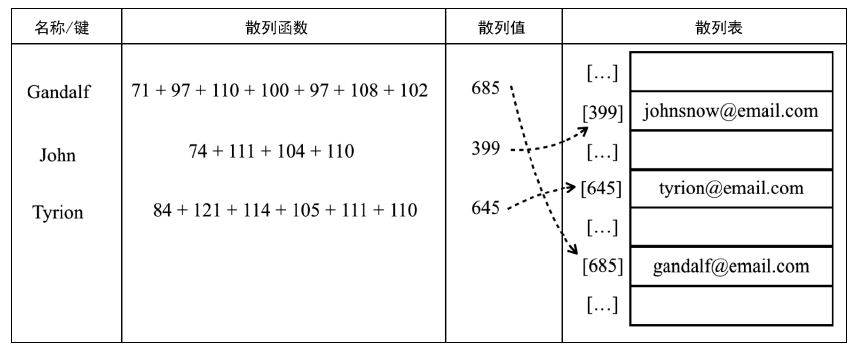
2.散列表 哈希表
HashMap 类,它是 Dictionary 类的一种散列表 实现方式。.散列算法的作用是尽可能快地在数据结构中找到一个值。
class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.table = {};
}
toStrFn(item) {
if (item === null) {
return "NULL";
} else if (item === undefined) {
return "UNDEFINED";
} else if (typeof item === "string" || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`;
}
return JSON.stringify(item);
}
myHashCode1(key) {
if (typeof key === "number") {
return key; //键是数字直接返回
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i); //获取阿斯克码值
}
//为了得到比较小的数值,我们会使用 hash 值和一个任意数做除法的余数
return hash % 37; //这个37可以随意设置
}
//社区推崇的算法,防止重复
myHashCode2(key) {
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 5381;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash = hash * 33 + tableKey.charCodeAt(i); //这里别忘了i,不然只会取首字母
}
return hash % 1013;
} //散列函数算法,把键转成散列值的数据
hashCode(key) {
return this.myHashCode2(key);
}
//其实就是set
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const valuePair = this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
remove(key) {
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
const valuePair = this.table[hash];
if (valuePair != null) {
delete this.table[hash];
return true;
}
return false;
}
}实例应用:

3. ES6的Map
var mymap = new Map();
var obj = { a: 1 };
mymap.set("name", "kerwin");
mymap.set({ a: 1 }, "aaaaaa");
mymap.set(obj, "aaaaaa"); //这样才能get到aaaaaa的值
mymap.get("name");
mymap.delete("name");其他方法:

weakmap只能以对象为键
八 . 树
树是一种分层数据的抽象模型。
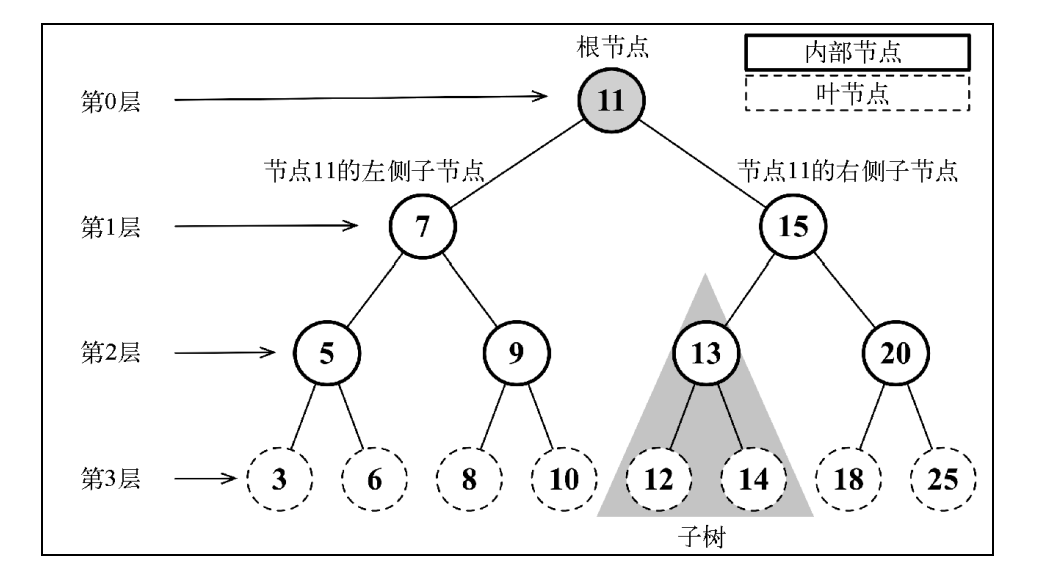
1. 二叉树
二叉树中的节点最多只能有两个子节点:一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点。
2. 二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树(BST)是二叉树的一种,但是只允许你在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值, 在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值。
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
EQUALS: 0,
}; //提前定好状态表示
//创建节点
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key; // 节点值
this.left = null; // 左侧子节点引用
this.right = null; // 右侧子节点引用
}
}
//二叉搜索树
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null; //Node 类型的根节点
}
insert(key) {
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
}
//递归迭代
insertNode(node, key) {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
//如果小于
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
} else {
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
}
//对比大小函数
compareFn(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
}2-1 遍历
- 中序遍历是一种以上行顺序访问 BST 所有节点的遍历方式,也就是以从最小到最大的顺序 访问所有节点。 中序遍历的一种应用就是对树进行排序操作。
- 先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点的。先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构化的文档。
- 后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身。后序遍历的一种应用是计算一个目 录及其子目录中所有文件所占空间的大小。
//中序遍历
inOrderMap(callback) {
this.inOrderMapNode(this.root, callback);
}
//用于递归
inOrderMapNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.inOrderMapNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.key); //对应值返回出来
this.inOrderMapNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
//先序遍历
preOrderMap(callback) {
this.preOrderMapNode(this.root, callback);
}
preOrderMapNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
callback(node.key);
this.preOrderMapNode(node.left, callback);
this.preOrderMapNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
//后序遍历
postOrderMap(callback) {
this.postOrderMapNode(this.root, callback);
}
postOrderMapNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.postOrderMapNode(node.left, callback);
this.postOrderMapNode(node.right, callback);
callback(node.key);
}
}
}先序遍历: 先根 再左 再右 中序遍历: 先左 再根 再右 后序遍历: 先左 再右 再根
2-2 查询
//找最小项
min() {
return this.minNode(this.root);
}
minNode(node) {
let current = node;
//不断while循环,改变指针指向,直到找到最左边的那一个节点
while (current != null && current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
//找最大项
max() {
return this.maxNode(this.root);
}
maxNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
search(key) {
return this.searchNode(this.root, key); //从根节点开始往下找
}
searchNode(node, key) { //左右双线并行
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return this.searchNode(node.left, key); //小于往左找
} else if (
this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN //大于往右找
) {
return this.searchNode(node.right, key);
} else {
return true;
}
}
}2-3 移除
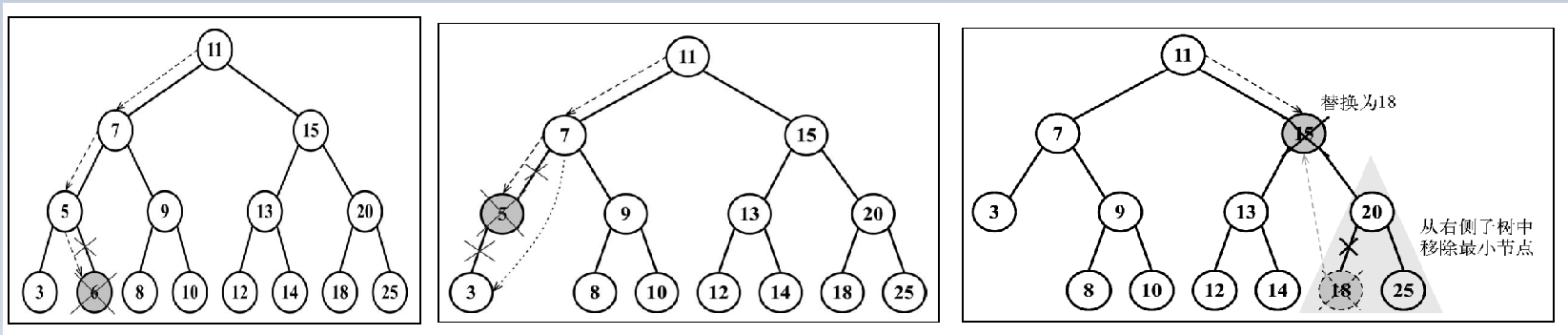
第三种情况要从右边找一个最小的替换,因为左边的最大要小于右边的最小
remove(key) {
this.root = this.removeNode(this.root, key);
}
removeNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
//下面是没有子节点了
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
} else if (
this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
} else {
//下面是有子节点的情况
// 键等于 node.key
// 第一种情况
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
node = null;
return node;
}
// 第二种情况 不用担心其中一个节点会比上个节点大
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
return node;
} else if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
return node;
}
// 第三种情况 以传入的节点开始找寻到临近最小的
const target = this.minNode(node.right);
node.key = target.key; //直接做值的替换
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, target.key);
return node;
}
}九. 二叉堆
二叉堆是一种特殊的二叉树,有以下两个特性。
- 它是一棵完全二叉树,表示树的每一层都有左侧和右侧子节点(除了最后一层的叶节点), 并且最后一层的叶节点尽可能都是左侧子节点,这叫作结构特性。
- 二叉堆不是最小堆就是最大堆。最小堆允许你快速导出树的最小值,最大堆允许你快速 导出树的最大值。所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)每个它的子 节点。这叫作堆特性。
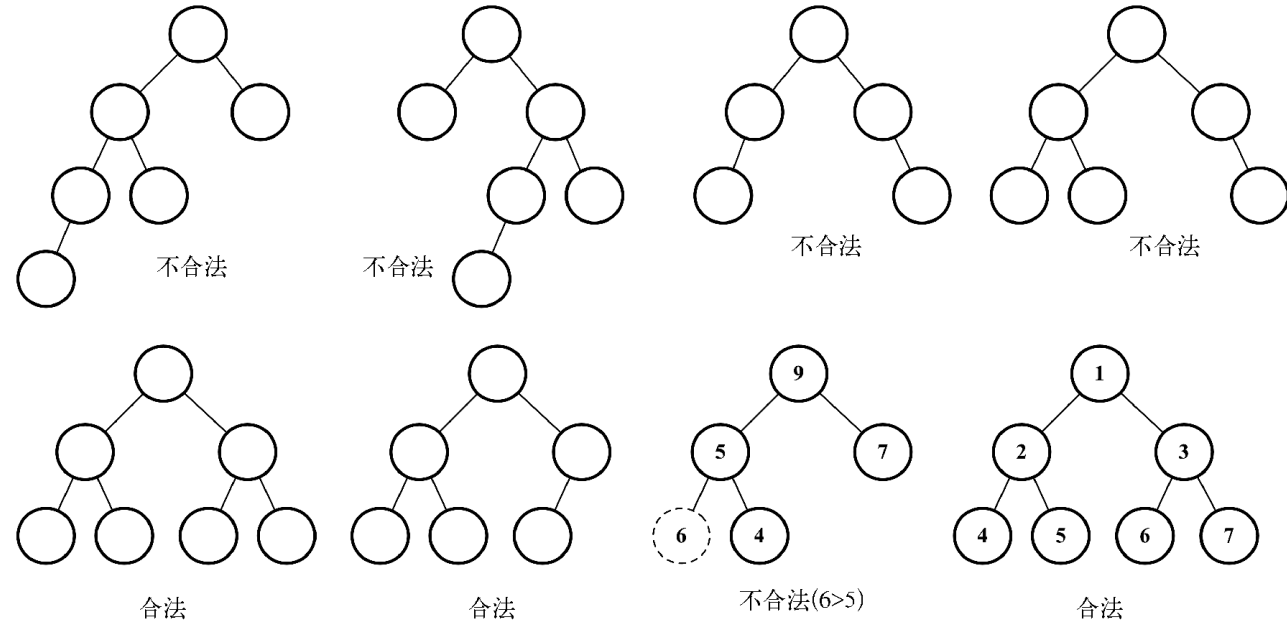
1. 最小堆 根节点最小
const Compare = {
less: -1,
bigger: 1,
equ: 0,
};
class MinHeap {
heap = [];
//给一个索引,找到索引对应的两个子节点
getLeftIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 1;
}
getRightIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 2;
}
//由传入的索引得到其父节点
getParentIndex(index) {
if (index === 0) {
return undefined;
}
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
this.heap.push(value); // {1}
//与父节点逐级对比,如果比父节点小,就交换位置 注意是逐级
this.siftUp(this.heap.length - 1); // {2}
return true;
}
return false;
}
compareFn(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.equ;
}
return a < b ? Compare.less : Compare.bigger;
}
siftUp(index) {
let parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
//while循环逐渐对比,一层层往上走,上调节点
while (
index > 0 &&
this.compareFn(this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]) === Compare.bigger //父比子大
) {
swap(this.heap, parent, index);
index = parent;
parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
}
}
//交换值
swap(array, a, b) {
const temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
}
//长度
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
//判空
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
//导出堆顶部元素
findTarget() {
return this.heap[0];
}
//删除
extract() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
const removedValue = this.heap[0]; //先找到要删除的结构
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop(); //不破坏结构 最后一个弹出覆盖在堆顶部
this.siftDown(0);
return removedValue;
}
//往下下溯
siftDown(index) {
let element = index;
const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const right = this.getRightIndex(index); //分别取出索引对应的左右子节点,下面将左右子节点对比,看谁更小
const size = this.size(); //注意别超出长度
if (left < size && this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[left]) === Compare.bigger) {
element = left;
//如果大, element 改变了
}
if (
//上面最新的element 与 右边进行对比
right < size &&
this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[right]) === Compare.bigger
) {
element = right;
}
if (index !== element) {
//如果最小的就是自己,就不用交换了
swap(this.heap, index, element);
this.siftDown(element);
}
}
}
function swap(array, a, b) {
const temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
}
var heap = new MinHeap();2. 最大堆
class MaxHeap extends MinHeap {
constructor() {
super();
}
//把方法覆盖 可以只改这个不改其他,也可以改其他一堆不改这个
compareFn(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.equ;
}
return a > b ? Compare.less : Compare.bigger;
}
}十. 排序算法
1. 冒泡排序
冒泡排序比较所有相邻的两个项,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换它们。元素项向上移动至 正确的顺序,就好像气泡升至表面一样,冒泡排序因此得名。
function bubbleSort(array) {
const { length } = array;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < length - 1 - i; j++) {
// -i是因为一次可以少比一次
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
swap(array, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
return array;
}
//外层控制数组每一个数,内层控制这个数与后面的每一个数进行比较后的位置交换
function swap(array, a, b) {
const temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
//也可以用解构: [array[a],array[b]] = [array[b],array[a]]
}2. 选择排序
选择排序算法是一种原址比较排序算法。选择排序大致的思路是找到数据结构中的最小值并 将其放置在第一位,接着找到第二小的值并将其放在第二位,以此类推。
function selectionSort(array) {
const { length } = array;
let indexMin;
for (let i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
indexMin = i;
for (let j = i; j < length; j++) {
if (array[indexMin] > array[j]) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
if (i !== indexMin) {
swap(array, i, indexMin);
}
}
return array;
}3. 插入排序
插入排序每次排一个数组项,以此方式构建最后的排序数组。
function insertionSort(array) {
const { length } = array;
let temp; //存当前这一轮对应索引的元素值
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
let j = i;
temp = array[i];
//当前值与前一个值做比较,如果当前值更小,则交换位置
while (j > 0 && array[j - 1] > temp) {
array[j] = array[j - 1];
j--;
}
array[j] = temp;
}
return array;
}4. 归并排序
归并排序是一种分而治之算法。其思想是将原始数组切分成较小的数组,直到每个小数组只 有一个位置,接着将小数组归并成较大的数组,直到最后只有一个排序完毕的大数组。
这个的动画看不懂不用看。
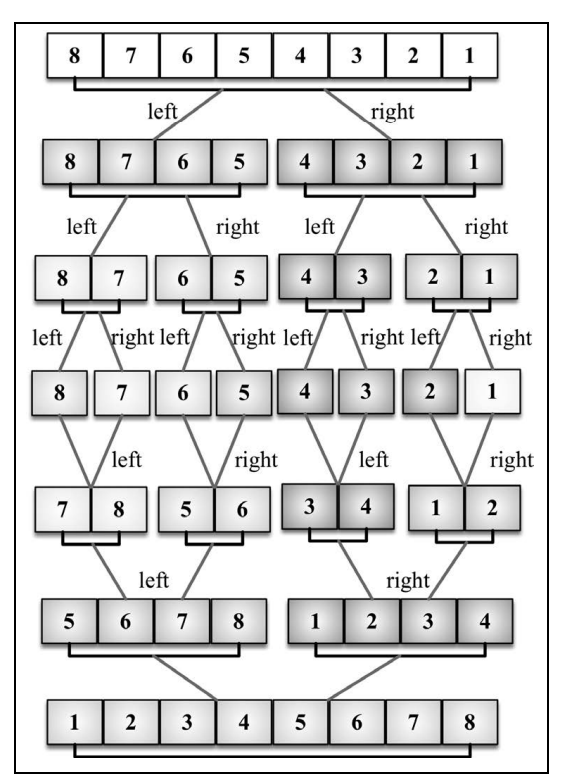
function mergeSort(array) {
if (array.length > 1) {
const { length } = array;
const middle = Math.floor(length / 2);
const left = mergeSort(array.slice(0, middle));
const right = mergeSort(array.slice(middle, length));
array = merge(left, right);
}
return array;
}
function merge(left, right) {
let i = 0;
let j = 0;
const result = [];
while (i < left.length && j < right.length) {
result.push(left[i] < right[j] ? left[i++] : right[j++]);
console.log(result);
//先push ,再++ 重要!!!
}
return result.concat(i < left.length ? left.slice(i) : right.slice(j));
}5. 快速排序
function quickSort(arr) {
const { length } = arr;
if (length < 2) {
return arr; //假设剩下2,1 以2为基准,此时要把1返回回来,所以要return
}
let base = arr[0];
let min = arr.slice(1).filter((item) => item <= base);
let max = arr.slice(1).filter((item) => item > base);
return quickSort(min).concat([base]).concat(quickSort(max));
}chrome的v8引擎就是用的快速排序算法实现的数组sort方法
6. 计数排序
计数排序使用一个用来存储每个元素在原始 数组中出现次数的临时数组。在所有元素都计数完成后,临时数组已排好序并可迭代以构建排序 后的结果数组。
function countingSort(array) {
if (array.length < 2) {
return array;
}
const maxValue = findMaxValue(array); //找到要排序的数组中的最大值
//这里找最大值也可以用: Math.max(...array)
const counts = new Array(maxValue + 1); //新数组长度设置为最大值加一
array.forEach((element) => {
if (!counts[element]) {
//取反为真,初始赋值为0
counts[element] = 0;
}
counts[element]++;
});
let sortedIndex = 0;
counts.forEach((count, i) => {
while (count > 0) {
array[sortedIndex++] = i; //先取值再加一
count--;
}
});
return array;
}
function findMaxValue(array) {
let max = array[0];
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] > max) {
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
countingSort([5, 7, 4, 9, 1]);7. 桶排序
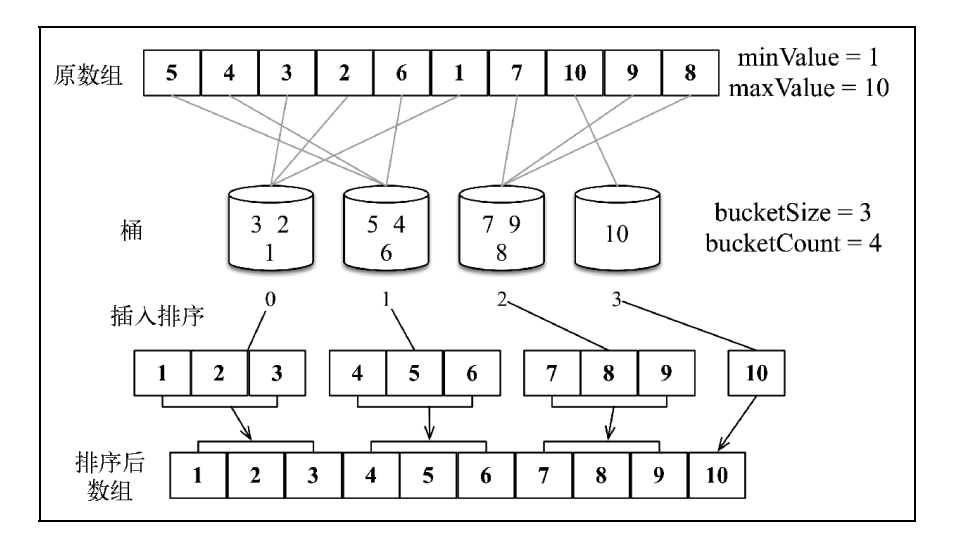
桶排序(也被称为箱排序)也是分布式排序算法,它将元素分为不同的桶(较小的数组), 再使用一个简单的排序算法,例如插入排序(用来排序小数组的不错的算法),来对每个桶进行 排序。然后,它将所有的桶合并为结果数组。
function insertSort(arr) {
const { length } = arr;
let temp; //存 当前这一轮对应索引的元素值
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0 && arr[j - 1] > temp) {
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
j--;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
console.log(arr);
}
// bucketSize = 3 代表初始一个桶里放三个元素
function bucketSort(array, bucketSize = 3) {
if (array.length < 2) {
return array;
}
const buckets = createBuckets(array, bucketSize);
//分桶装
return sortBuckets(buckets);
}
function createBuckets(array, bucketSize) {
let minValue = array[0];
let maxValue = array[0];
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] < minValue) {
minValue = array[i];
} else if (array[i] > maxValue) {
maxValue = array[i];
}
} //一次循环找到最小最大值
const bucketCount = Math.floor((maxValue - minValue) / bucketSize) + 1; // 最后一个索引+1 这里是得到桶的个数 其实也是得到最大桶的索引
const buckets = [];
for (let i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) {
buckets[i] = []; //创建空桶
}
//上面的也可以写成:
//const buckets = [...Array(bucketCount)].map(()=>[]) 映射成空数组
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
const bucketIndex = Math.floor((array[i] - minValue) / bucketSize);
//数组的每一项减去最小值除以桶的长度 然后把对应的数组项放到不同的桶里
buckets[bucketIndex].push(array[i]);
}
return buckets;
}
//把二维数组展开排序 使用插入排序算法
function sortBuckets(buckets) {
const sortedArray = [];
for (let i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
if (buckets[i] != null) {
insertSort(buckets[i]); //小桶内部数据排序
sortedArray.push(...buckets[i]);
}
}
return sortedArray;
}
bucketSort([5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 1, 7, 10, 9, 8]);8. 基数排序
基数排序也是一个分布式排序算法,它根据数字的有效位或基数(这也是它为什么叫基数排 序)将整数分布到桶中。基数是基于数组中值的记数制的。
十个桶,每个桶贴一个数字,先从个位开始筛选,各位数字和桶上数字相同,就放进去,然后再从十位数开始筛选,以此类推
const arr = [35, 2, 26, 2, 5, 8, 34, 1, 56, 99, 33];
const radixSort = (arr = []) => {
const base = 10;
let divider = 1;
let maxVal = 0;
while (divider === 1 || divider <= maxVal) {
const buckets = [...Array(10)].map(() => []);
for (let val of arr) {
buckets[Math.floor((val / divider) % base)].push(val);
maxVal = val > maxVal ? val : maxVal;
}
arr = [].concat(...buckets); //这里记得重新赋值
console.log(arr);
divider *= base;
}
return arr;
};十一. 搜索算法
1. 顺序搜索
顺序或线性搜索是最基本的搜索算法。它的机制是,将每一个数据结构中的元素和我们要找 的元素做比较。顺序搜索是最低效的一种搜索算法。
function sequentialSearch(array, value) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (value === array[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
sequentialSearch([3, 2, 1], 2);2.二分搜索
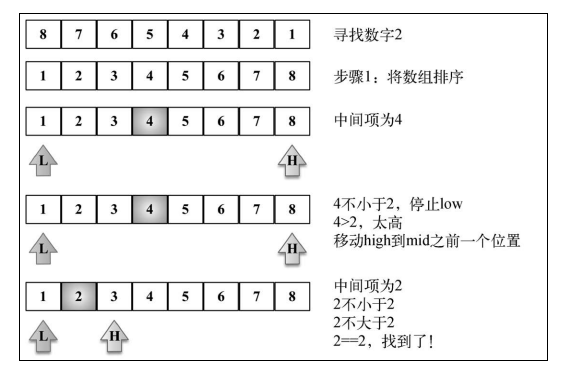
var Arr = [5, 7, 4, 2, 9];
function binarySearch(find, arr, low, high) {
arr = quickSort(arr);
if (low <= high) {
//这里写的有问题。详情看下面图片
if (arr[low] == find) {
return low;
}
if (arr[high] == find) {
return high;
}
var mid = Math.ceil((high + low) / 2); //操作的数组始终不变
if (arr[mid] == find) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] > find) {
return binarySearch(find, arr, low, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearch(find, arr, mid + 1, high);
}
}
return -1;
}
binarySearch(9, Arr, 0, Arr.length - 1);

3.内插搜索
内插搜索是改良版的二分搜索。二分搜索总是检查 mid 位置上的值,而内插搜索可能会根 据要搜索的值检查数组中的不同地方。
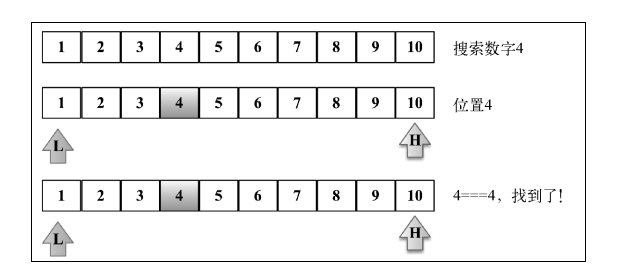
var arr = [5, 7, 4, 2, 9];
function InsertionSearch(arr, val, start, end) {
arr = quickSort(arr);
var end = end || arr.length - 1;
var start = start || 0;
if (start <= end && val >= arr[start] && val <= arr[end]) {
var mid = start + Math.floor(((val - arr[start]) / (arr[end] - arr[start])) * (end - start)); //和二分的区别就是这一句算法
if (arr[mid] == val) {
return mid;
}
if (arr[mid] > val) {
return InsertionSearch(arr, val, start, mid - 1);
} else {
return InsertionSearch(arr, val, mid + 1, end);
}
}
return -1;
}
InsertionSearch(arr, 2);不论是二分还是内插,返回的都是排好序的索引
内插其实就是算要查的数在数组中大概占多少比例,占0.4,表示大概在4的位置
十二. 随机算法
迭代数组,从最后一位开始并将当前位置和一个随机位置进行交换。这个随机位 置比当前位置小。这样,这个算法可以保证随机过的位置不会再被随机一次
function shuffle(array) {
for (let i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
swap(array, i, randomIndex);
}
return array;
}

十三.算法设计
1.分而治之
分而 治之是算法设计中的一种方法。它将一个问题分成多个和原问题相似的小问题,递归解决小问题, 再将解决方式合并以解决原来的问题。
分而治之算法可以分成三个部分。
(1) 分解原问题为多个子问题(原问题的多个小实例)。
(2) 解决子问题,用返回解决子问题的方式的递归算法。递归算法的基本情形可以用来解决子 问题。
(3) 组合这些子问题的解决方式,得到原问题的解。
归并和桶排序就是分而治之
2.动态规划
动态规划(dynamic programming,DP)是一种将复杂问题分解成更小的子问题来解决的优 化技术。
用动态规划解决问题时,要遵循三个重要步骤:
(1) 定义子问题;
(2) 实现要反复执行来解决子问题的部分;
(3) 识别并求解出基线条件。
子问题之间相互依赖
2-1 背包问题
背包问题是一个组合优化问题。它可以描述如下:给定一个固定大小、能够携重量 W 的背 包,以及一组有价值和重量的物品,找出一个最佳解决方案,使得装入背包的物品总重量不超过 W,且总价值最大。
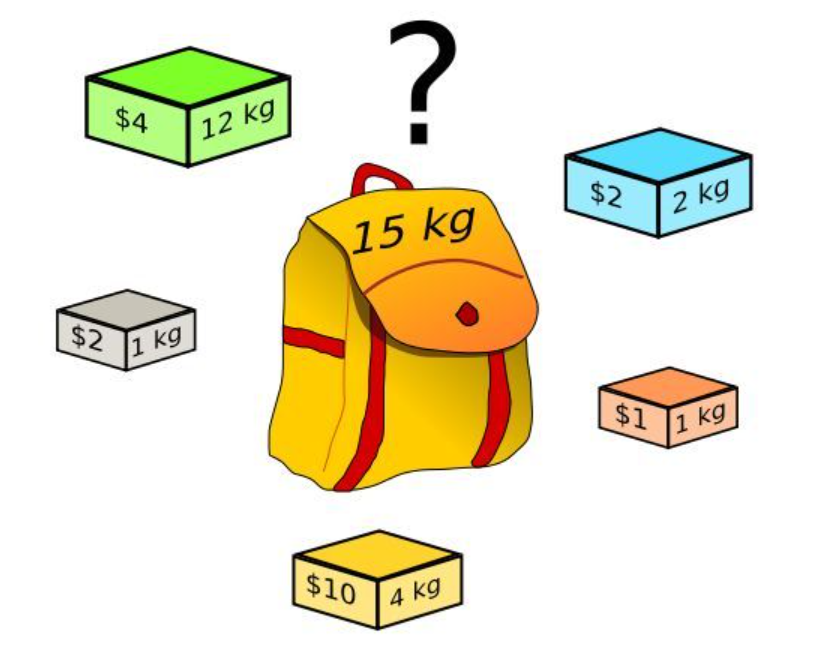
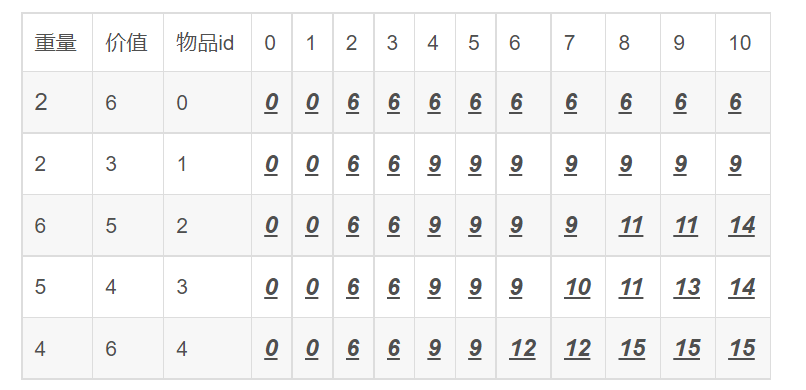
function knapSack(weights, values, W) {
var n = weights.length;
var f = new Array(n);
f[-1] = new Array(W + 1).fill(0); //第-1个物品,
//负一行的出现可以大大减少了在双层循环的分支判定。
// console.log(f)
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i] = new Array(W).fill(0);
for (var j = 0; j <= W; j++) {
if (j < weights[i]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
} else {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - weights[i]] + values[i]); //case 3
} //即使i = 0 也不怕,i-1 为-1 有-1行不怕
}
}
return f[n - 1][W];
}右下角就是最大值
下面是另一种写法

2-2 最长公共子序列
找出两个字符 串序列的最长子序列的长度。最长子序列是指,在两个字符串序列中以相同顺序出现,但不要求 连续(非字符串子串)的字符串序列。
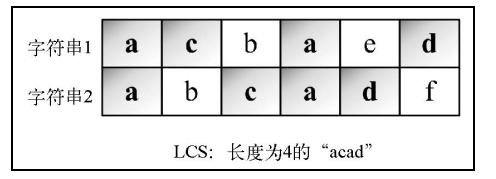
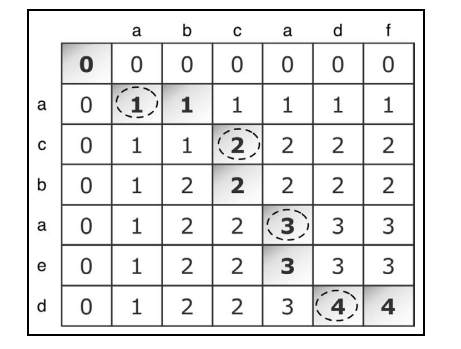
a和a比,a和ab比,a和abc比,a和abca比 以此类推
ac和a比,ac和abc比,ac和abca比 依次类推
如果横轴纵轴对应字符一致,就取交点的左上角值加1 比如ac和abc比,就是取a-b交点值1加一
如果横轴纵轴对应字符不一致,就取交点左边或上边的较大值,比如d-f的交点
function LCS(str1, str2) {
var m = str1.length;
var n = str2.length;
var dp = [new Array(n + 1).fill(0)]; //第一行全是0
for (var i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
//一共有m+1行
dp[i] = [0]; //第一列全是0
for (var j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
//一共有n+1列
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
//注意这里,str1的第一个字符是在第二列中,因此要减1,str2同理
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; //对角+1
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
console.log(LCS("abcadf", "acbaed"));3. 贪心算法
在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,他所做出的仅是在某种意义上的局部最优解。贪心算法不是对所有问题都能得到整体最优解,但对范围相当广泛的许多问题他能产生整体最优解或者是整体最优解的近似解。
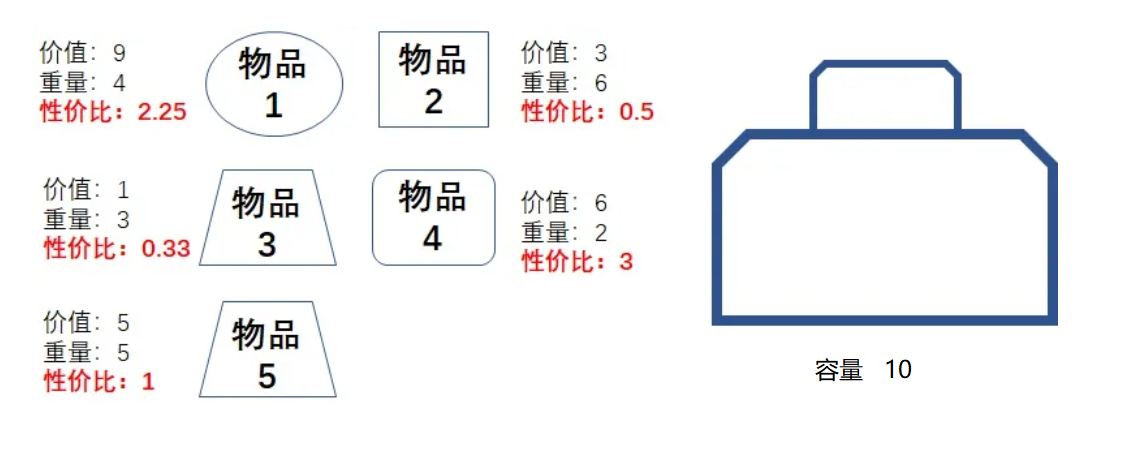
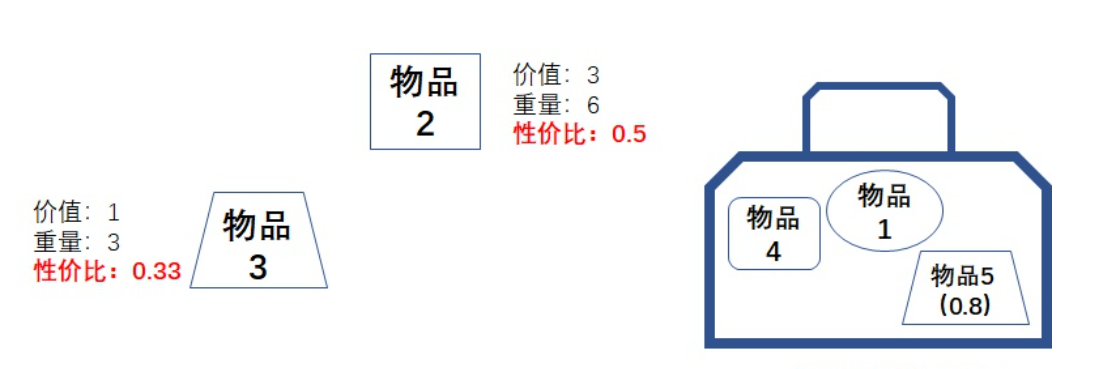
先算性价比,然后把性价比从高到底排列,依次放入,如果超出就取百分比
function tanx(capacity, weights, values) {
var list = [];
for (var i = 0, len = weights.length; i < len; i++) {
list.push({
num: i + 1, //第几件商品
w: weights[i], //重量
v: values[i],
rate: values[i] / weights[i]
});
}
list.sort(function (a, b) {
return b.rate-a.rate
});
// console.log(list)
var selects = [];
var total = 0;
for (var i = 0, len = list.length; i < len; i++) {
var item = list[i];
if (item['w'] <= capacity) {
selects.push({
num: item.num,
rate: 1, //完整的商品记录为1
v: item.v,
w: item.w
});
total = total + item.v;
capacity = capacity - item.w;
} else if (capacity > 0) {
//选取不完整的商品
var rate = capacity / item['w']; //可以放的比例
var v = item.v * rate;
selects.push({
num: item.num,
rate: rate,
v: item.v * rate,
w: item.w * rate
});
total = total + v;
break;
} else {
break;
}
}
return {
selects,
total
}
}4.回溯算法
回溯法采用试错的思想,它尝试分步的去解决一个问题。在分步解决问题的过程中,当它通过尝试发现现有的分步答案不能得到有效的正确的解答的时候,它将取消上一步甚至是上几步的计算,再通过其它的可能的分步解答再次尝试寻找问题的答案。
题目
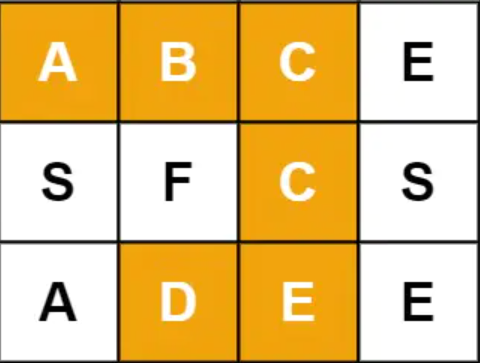
给定一个 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成 二维数组: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], 目标: word = "ABCCED"
function exist(board, word) {
let row = board.length;
let col = board[0].length;
for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {
const ret = find(i, j, 0);
if (ret) {
return ret;
}
}
}
return false;
function find(r, c, cur) {
if (r >= row || r < 0) return false;
if (c >= col || c < 0) return false;
if (board[r][c] !== word[cur]) return false;
if (cur == word.length - 1) return true;
let letter = board[r][c];
board[r][c] = null;
const ret =
find(r - 1, c, cur + 1) ||
find(r + 1, c, cur + 1) ||
find(r, c - 1, cur + 1) ||
find(r, c + 1, cur + 1);
//用null做标记是避免重复查找
board[r][c] = letter;
return ret;
}
}十四. 算法复杂度
O 表示法用于描述算法的性能和复杂程 度。O 表示法将算法按照消耗的时间进行分类,依据随输入增大所需要的空间/内存。

- O(1)
function inc(n) {
return ++n;
}- O(n)
function search(arr, value) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === value) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}- O(n2 )
function bubbleSort(array) {
const { length } = array;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
//交换位置的方法
swap(array, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
console.log(array);
}